Determining which drivers your system uses requires a few steps. We’ll use Windows Device Manager for this purpose.
For Windows 8 or Windows 10, right-click the Windows Start button. Find and select Device Manager, as illustrated below.
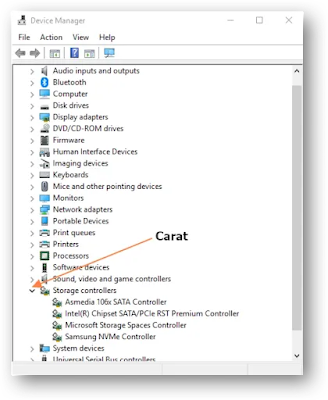
Once the Device Manager is open, find and select the carat (>) that precedes Storage Controllers to expand the listing of all Storage Controller devices in the computer as illustrated below.
NOTE: If exclamation marks are shown in the Device Manager, it means a problem exists with that device. In all likelihood, it is a driver issue that you should be able to correct by installing updated drivers or rolling back to previous drivers. You’ll need to correct the issue before continuing.
As you can see in the graphic above, there are four Storage Controllers on this computer. In this example, our interest is in the Intel Chipset SATA/PCIe RST Premium Controller, as this is used for the RAID array on this machine.
To determine which driver is used, double-click on the desired Storage Controller entry. This will display the Properties window. You’ll then select the Driver tab, as illustrated below.
Write down the Driver Date and the Driver Version found here for future reference. In our example, we find:
Driver Date: 8/7/2017 Driver Version 15.8.1.1007
Click on the Details tab of the Properties window and select Inf name from the drop-down menu under Property.
We now know that our driver for the Intel Storage Controller is:
OEM 32.inf Dated 8/7/2017 Version 15.8.1.1007
How do we find where this driver is in our installed Windows OS? We’ll use some built-in Windows tools using an Admin Command Prompt. The easiest way to open an Admin Command Prompt is using the Search feature of Windows:
Type Command into the Search box on the Task bar
Find Command Prompt in the next menu
Hover your cursor over the entry
Right-click and select Run as administrator
When the Command Prompt opens it will appear as illustrated below.
NOTE: The path C:\Windows\system32> indicates the prompt is open as an Administrator. If you see something else on your screen, then you do not have an Admin Command Prompt open. You will need to find out how to do so on your computer.
In our example, we find that the Original name of our Storage Controller driver is iastorac.inf. We will use this name and the Command prompt to locate the driver. To locate the Storage Controller driver, use the Dir command at the command prompt. To start a clean work space, you can clear the command prompt window by typing cls and pressing the Enter key. At the flashing prompt, type dir infname /s. In our example, we would type dir iastorac.inf /s and then press Enter. You should see a result similar to the one below.
sources# acronis.com








Post a Comment